N-1 Perfusion
A form of seed train intensification, N-1 perfusion refers to the intensification of cell growth in the seed train step (N-1) before the production bioreactor (N), achieving a more rapid and robust process while maintaining an existing Fed-Batch based production scheme.

N-1 perfusion is done by attaching a cell retention device, such as the XCell ATF® Device, to the N-1 bioreactor to attain high cell density and viability. This seeds the N production bioreactor at a higher starting cell density and shortens the production bioreactor run time. The process dramatically increases facility output without direct change to the core Fed-Batch production process. A robust cell retention device is required to attain a high cell density inoculum for the production bioreactor.
The combination of implementation ease and productivity increase makes N-1 perfusion the most frequent starting point for upstream intensification. Once in place, further intensify the seed train by adding High Productivity Harvest (HPH) to the N bioreactor or transition to continuous.
Repligen solutions help overcome key challenges in N-1 perfusion, with hands-on process and implementation consultation from global Field Applications Specialists.
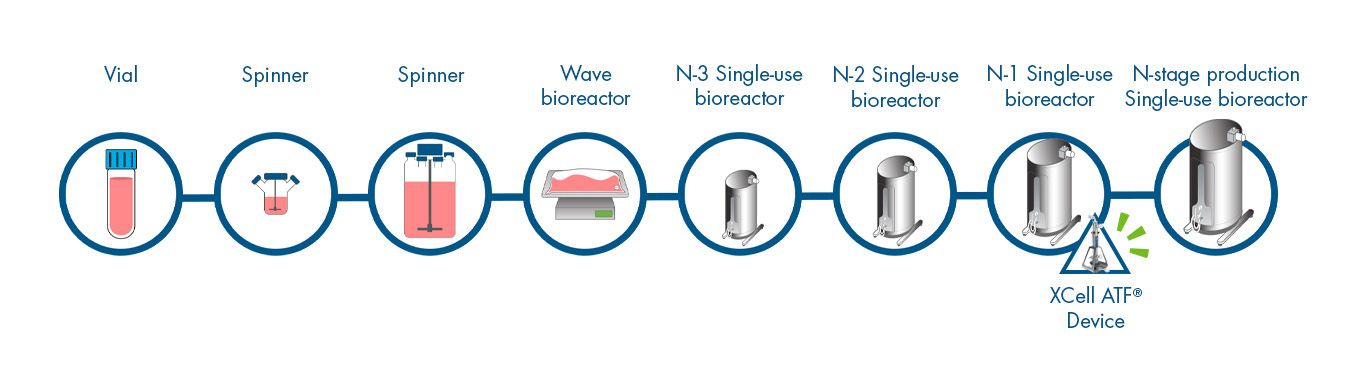
N-1 Perfusion Cell Culture Workflow
Click on the workflow link below to find productivity and throughput solutions you can implement today.
Boost throughput, save time
N-1 perfusion intensifies the Fed-Batch process, increasing facility throughput. Seeded at a higher initial density, cells in the N bioreactor grow faster, reach a higher max VCD and produce more product than traditional Fed-Batch. Harvest sooner and increase the number of batches per year as compared to a standard Fed-Batch process. Alternatively, maintain the N bioreactor run time to increase overall yield.
Maintain a Fed-Batch process
N-1 perfusion intensification increases N bioreactor productivity and throughput while maintaining a Fed-Batch process. No perfusion or media exchange of the N bioreactor is required, allowing the N bioreactor to maintain a single and discreet Fed-Batch harvest point.
Minimize validation impact
Intensify with minimal process modifications and regulatory edits. No additional equipment is connected to the N bioreactor, no media exchange occurs during the production run and cell viability is higher, typically leading to lower impurity values.
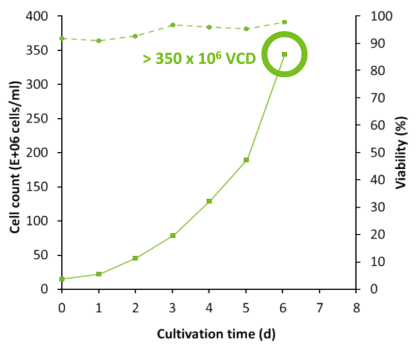
N Bioreactor reached 350 x 106 VCD
N-1 perfused Fed-Batch reached 350 million cells/mL VCD in just 6 days. In comparison, standard Fed-Batch achieved 30 million cells/mL viable cell density (VCD) over a course of 14 days. Productivity of the N bioreactor with N-1 perfusion increased 20X while maintaining viability above 90%.
Higher cell density and viability
- 10X VCD over Fed-Batch
- VCD as high as 350 x 106 cells/mL
- 50% reduction in production time
- 20X increase in productivity
- Lower COGs
N-1 Perfusion increased VCD 10X, reduced production time by 50%
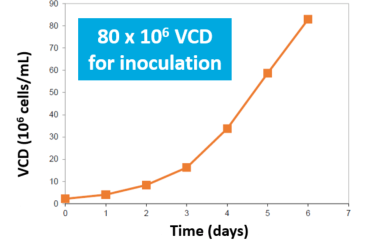
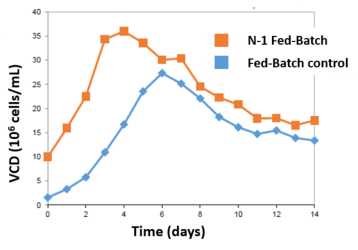
The perfused N-1 bioreactor cell density rapidly increased from 8 to 80 million cells/mL (10x VCD) in 4-5 days. Inoculation of the N bioreactor with the N-1 perfused culture established a 10X higher initial viable cell density over Fed-Batch (A). After 3 days, the N-1 inoculated bioreactor achieved 35 million VCD. In comparison, the control required 6 days to achieve 25 million VCD (B).
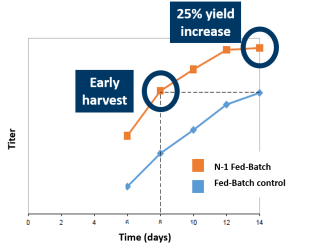
Leverage higher VCD to either increase throughput or increase yield. Harvest of the N-1 Fed-Batch bioreactor at day 8 was equivalent to harvesting the Fed-Batch control at day 14, saving 6 days of N bioreactor suite time (C). Alternatively, harvest the N-1 Fed-Batch process at day 14 for a 25% overall yield increase.
- N-1 bioreactor reached 10X VCD in 4-5 days
- N-1 perfused Fed-Batch bioreactor reached maximum VCD of 35 million compared to 25 million with traditional Fed-Batch
- Maximum VCD was achieved 3 days earlier
- Harvest 6 days earlier for same yield OR
- Achieve 25% yield increase by day 14
N-1 Bioreactor VCD
Production Bioreactor VCD
Production Bioreactor

Customer First.
Support is part of the Repligen DNA. Our goal is to provide exceptional customer experience, and to support the efficient and successful adoption and implementation of all Repligen products and services.
- Field Application Support
- Customer Service
- Field Service Engineers