NGL-Impact® A ELISA Kit Performance Summary
INTRODUCTION
The Repligen NGL-Impact® A ELISA kit (Catalog number 9222-1) is intended for the detection and quantitation of residual NGL-Impact® Protein A. It was been developed for users who require a highly sensitive assay to measure small amounts of contaminating NGL-Impact® A in antibody products. Testing for NGL-Impact® A contamination occurs in several different phases of development and commercial manufacturing which may include:
- Process development for leaching characteristics of the resin under specific conditions
- Manufacturing, typically from eluted samples taken throughout several points in the purification process
- Finish product release to document process containment levels and lot-to-lot consistency
The following summary report contains performance data collected from the evaluation of the NGL-Impact® A ELISA Kit in the presence of human Immunoglobulin G (hIgG). The data presented here demonstrates the following:
- Ability to detect NGL-Impact® A in the presence of up to 0.5 mg/ml hIgG in a PBS-T buffer using Dilute & Go method, or sample up to 10 mg/ml hIgG by Boil & Boost method
- Percent recovery (Accuracy), inter- and intra-assay precision, limit of quantitation and limit of detection
RESULTS SUMMARY
NGL-Impact® A in the presence of hIgG
The performance of the Repligen NGL-Impact® A ELISA kit was evaluated when detecting NGL-Impact® A in the presence of hIgG compared to a standard containing no hIgG. NGL-Impact® A spiked samples had a starting hIgG concentration of 0.5 mg/ml when diluted into the assay plate or had a 10 mg/ml hIgG initial concentration when using boiling method. Each spike sample was prepared in replicates of 3 and ELISA was performed according to the Kit’s standard protocol.
Data Handling
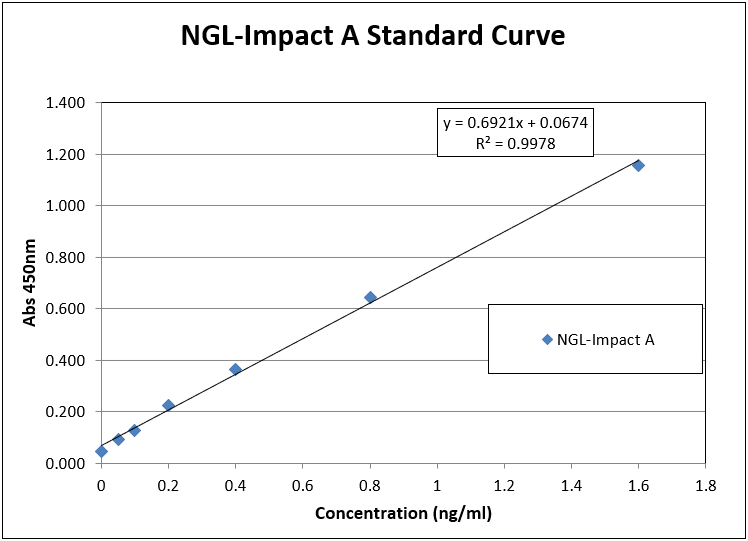
Standard curve data points were fitted to linear regression line. This equation allowed back-calculation of sample NGL-Impact® A concentrations and calculation of LoQ values. Percent recovery was calculated as follows:
% Recovery = Calculated Conc X100
Theoretical Conc
Intra-Assay Precision
Table 1. Intra-Assay Precision for Standard Curve samples (without hlgG)
| Conc (ng/ml) | Avg % CV |
|---|---|
| 1.6 | 0.8 |
| 0.8 | 5.3 |
| 0.4 | 2.0 |
| 0.2 | 1.3 |
| 0.1 | 5.7 |
| 0.05 | 7.1 |
Table 2. Intra-Assay Precision for samples containing hlgG by Dilute & Go
| Conc (ng/ml) | Calculated Conc | Avg % CV |
|---|---|---|
| 1.0 | 1.09 | 1.0 |
| 0.5 | 0.58 | 2.6 |
| 0.25 | 0.26 | 2.4 |
Table 3. Intra-Assay Precision for samples containing hlgG by Boil & Boost
| Conc (ng/ml) | Calculated Conc | Avg % CV |
|---|---|---|
| 1.0 | 1.10 | 3.4 |
| 0.5 | 0.50 | 3.5 |
| 0.25 | 0.24 | 1.6 |
Inter-Assay Percision
Table 4. Inter-Assay Precision for Standard Curve samples (without hlgG)
| Conc (ng/ml) | Avg % CV |
|---|---|
| 1.6 | 1.0 |
| 0.8 | 3.1 |
| 0.4 | 3.2 |
| 0.2 | 2.6 |
| 0.1 | 7.2 |
| 0.05 | 21.1* |
*Conc. is below LLOQ
Table 5. Inter-Assay Precision for sample containing hlgG by Dilute & Go
| Conc (ng/ml) | Calculated Conc | Avg % CV |
|---|---|---|
| 1.0 | 1.09 | 6.2 |
| 0.5 | 0.58 | 2.4 |
| 0.25 | 0.26 | 5.5 |
Table 6. Inter-Assay Precision for samples containing hlgG by Boil & Boost
| Conc (ng/ml) | Calculated Conc | Avg % CV |
|---|---|---|
| 1.0 | 1.10 | 3.7 |
| 0.5 | 0.50 | 7.5 |
| 0.25 | 0.24 | 4.7 |
Accuracy
Table 7. Accuracy for Standard Curve samples
| Conc (ng/ml) | Avg % Error | Avg % Recovery |
|---|---|---|
| 1.6 | -2.5 | 97.5 |
| 0.8 | 6.3 | 106.3 |
| 0.4 | 14.2 | 114.2 |
| 0.2 | 8.6 | 108.6 |
| 0.1 | -10.6 | 89.4 |
| 0.05 | -51.6* | 48.4* |
*Conc. is below LLOQ
Table 9. Accuracy for samples containing hlgG by Boil & Boost
| Conc (ng/ml) | Avg % Error | Avg % Recovery |
|---|---|---|
| 1.0 | 9.8 | 109.8 |
| 0.5 | 0.1 | 100.1 |
| 0.25 | -5.6 | 94.4 |
Table 8. Accuracy for samples containing hlgG by Dilute & Go
| Conc (ng/ml) | Avg % Error | Avg % Recovery |
|---|---|---|
| 1.0 | 8.6 | 108.6 |
| 0.5 | 15.1 | 115.1 |
| 0.25 | 3.7 | 103.7 |
Limit of Quantitation (LoQ)
The LoQ determined from the standard curve with no IgG present was calculated to be 0.07 ng/ml. The LoQ for the NGL-Impact® A spiked samples in the presence of hIgG was 0.87 ppm when using Dilute & Go method and 0.048 ppm for Boil & Boost method.
Limit of Detection (LoD)
The LoD determined from the standard curve was calculated to be 0.06 ng/ml. The LoQ for the NGL-Impact® A spiked samples in the presence of hIgG was 0.64 ppm using Dilute & Go and 0.04 ppm for Boil & Boost.
Linearity of Dilution
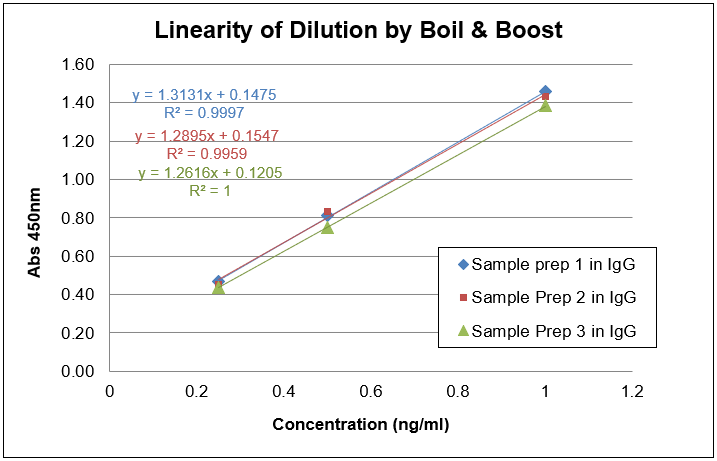
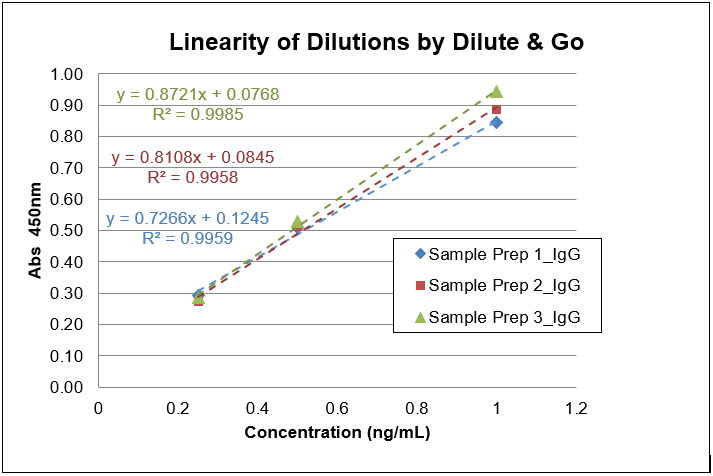
Figure 1. Linearity of dilution graph showing high correlation of accuracy throughout the range of concentrations tested with presence of IgG by both Dilute & Go and Boil & Boost methods.
CONCLUSIONS
Intra-assay data indicated that precision for the standard curve samples were within acceptable parameters with % CV values ranging from 0.8-7.1%. Intra-assay data indicated that samples were assayed with relative accuracy and precision.
Inter-assay data indicated that data was reproducible. The coefficient of variation between assays was less than or equal to 7.2% for concentrations equal to and above the LoQ. The samples inter-assay precision was in the range of 2.4-7.5%.
Accuracy for concentrations above LoQ, gauged by % relative error, was from -10.6 to 14.2 for standards, and from -5.6 to 15.1 for samples assayed in Dilute & Go method and Boil & Boost methods.
The LoQ determined from the standard curve with no IgG present was calculated to be 0.07 ng/ml. The LoQ for the NGL-Impact® A spiked samples in the presence of hIgG was 0.87 ppm when using Dilute & Go method and 0.048 ppm for Boil & Boost method.
The LoD determined from the standard curve was calculated to be 0.06 ng/ml. The LoQ for the NGL-Impact® A spiked samples in the presence of hIgG was 0.64 ppm using Dilute & Go and 0.04 ppm for Boil & Boost.
All sample concentrations equal to and above the LoQ had % CV values from 1.0-3.5%, below the 15% limit.
EXPLANATION OF CALCULATIONS
Precision (%CV)
Precision was calculated by determining the standard deviation between NGL-Impact® A spiked sample data points and dividing by the mean value. According to the ‘Guidance for Industry: Bio-analytical Method Validation’ text, precision should be within 15%.
Intra-Assay Precision
The intra-assay precision was calculated for each NGL-Impact® A spiked sample concentration by averaging the %CV values across all assays.
Inter-Assay Precision
The inter-assay precision was calculated for each concentration point by determining the standard deviation between calculated results from each of the three assays, then dividing by the mean value.
Limit of Quantitation (LoQ)
The limit of quantitation (LoQ) was defined as 10 times the standard deviation of 0 ng/ml sample. The standard deviation of the 0 ng/ml OD value was multiplied by 10 then added to base 0 ng/ml OD value. The LoQ was then generated by entering the summed value into the linear equation. For each kit the LoQ was reported as ng NGL-Impact® A per ml (ng/ml) buffer, and ng NGL-Impact® A per mg hIgG (ppm) for NGL-Impact® A spiked samples run in presence of hIgG.
Limit of Detection (LoD)
The limit of detection (LoD) was defined as 3 times the standard deviation of 0 ng/ml Protein A sample. The standard deviation of the 0 ng/ml OD value was multiplied by 3 then added to base 0 ng/ml OD value. The LoD was then generated by entering the summed value into the standard curve equation. For each kit a LoD was reported as ng NGL-Impact® A per ml (ng/ml) buffer and in parts per million (ppm) against IgG concentration.
Accuracy
Accuracy is described as the % recovery determined by the assay compared to the theoretical spiked concentration.
Example standard curve